Proper pool care is the key to a long lifespan, so you should choose the pool chemicals and use them correctly. Otherwise, you risk your health (skin and eyes irritation, or even an infection) and shorten the life of your pool from a few decades to a few years.
As someone who has worked in the pool and hot tub service and supply industry for over ten years, I know by heart the list of required pool chemicals and the chemical levels. Therefore, I want to share my experience so that you do not spend too much personal time searching for the necessary information and can read a ready-made list of pool chemicals in our article.
Must-Have Chemicals For Your Pool
| Sanitizers | |
 In The Swim Stabilized Chlorine for Sanitizing Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.6 Item form: Tablets Net weight: 50 lbs. Active ingredients: 99% trichlor Packaging: Plastic bucket | Purpose It can dissolve in water, and when it does, it creates a substance-free available chlorine (FAC), which helps sanitize the pool or spa. Consumption One 3-inch tablet can treat up to 10,000 gallons to maintain 1–3 of Jump to the detailed review |
 In The Swim Bromine Sanitizer Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.6 Item form: Tablets Net weight: 50 lbs. Active ingredients: 96% bromochlorodimethylhydantoin and 4% other ingredients Packaging: Plastic bucket | Purpose It releases hypochlorous acid (HOCl) when dissolved in water, which acts as a disinfectant by destroying microorganisms like bacteria and viruses. Consumption 31 1-inch tablets can treat up to 10,000 gallons to maintain 3–5 ppm of Jump to the detailed review |
| Pool Shock or Oxidizers | |
 HTH Super Shock Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.7 Item form: Powder Net weight: 12 lbs. Active ingredients: 56.44% calcium hypochlorite and 43.56% other ingredients Packaging: Plastic bag | Purpose A highly concentrated dose of chlorine that is used to kill large numbers of algae and bacteria at once and rapidly raise available chlorine levels. Consumption 12 lbs. can treat up to 13,500 gallons to maintain 1–4 ppm of available chlorine Jump to the detailed review |
 In The Swim Chlorine-Free Pool Shock Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.7 Item form: Powder Net weight: 40 lbs. Active ingredients: 38% potassium peroxymonosulfate and 62% other ingredients Packaging: Plastic bucket | Purpose A powerful oxidizing agent that oxidizes and breaks down organic matter in water. Can be used with bromine sanitizer, which will totally break bacteria and viruses. Consumption 1 lb. can treat up to 10,000 gallons to increase the available chlorine level by 5 ppm Jump to the detailed review |
| Stabilizer or Conditioner | |
 Pool Mate Stabilizer and Conditioner Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.6 Item form: Powder Net weight: 7 lbs. Active ingredients: 100% cyanuric acid Packaging: Plastic bag | Purpose Prevents the breakdown of chlorine by sunlight, forming a shield around the chlorine molecules. Consumption For 10,000-gallon pools: add 12.5 oz. to increase by 10 ppm; add 1.6 lbs. to increase by 20 ppm; add 2.3 lbs. to increase by 30 ppm; add 3.1 lbs. to increase by 40 ppm; add 3.9 lbs. to increase by 50 ppm Jump to the detailed review |
| pH & Total Alkalinity Adjusters | |
 Clorox Pool&Spa pH Up Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.7 Item form: Granular Net weight: 4 lbs. Active ingredients: 100% sodium carbonate Packaging: Plastic bag | Purpose It has a high pH, which makes it effective in pH adjusting in swimming pools. Consumption For 10,000-gallon pools: add 12 oz. to increase pH from 6.8–7.1 to 7.2–7.6; add 16 oz. to increase pH from 6.5–6.7 to 7.2–7.6; add 30 oz. to increase pH from 6.4 and below to 7.2–7.6 Jump to the detailed review |
 Clorox Pool&Spa pH Down Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.7 Item form: Granular Net weight: 5 lbs. Active ingredients: 93.2% sodium bisulfate and 6.8% other ingredients Packaging: Plastic bag | Purpose It is commonly used in the treatment of swimming pools to lower the pH of the water, as it reacts with water to form acid. Consumption For 10,000-gallon pools: add 6 oz. to lower pH from 7.7–7.8 to 7.2–7.6; add 12 oz. to lower pH from 7.9–8.0 to 7.2–7.6; add 20 oz. to lower pH from 8.1–8.4 to 7.2–7.6; add 24 oz. to lower pH from 8.5 and above to 7.2–7.6 Jump to the detailed review |
 Clorox Pool&Spa Alkalinity Increase Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.7 Item form: Granular Net weight: 5 lbs. Active ingredients: 100% sodium hydrogen carbonate Packaging: Plastic bag | Purpose It can help to raise the pH level, making the water more alkaline and reducing acidity. This can help to prevent the problems associated with low pH levels and ensure that the water remains clean, clear, and safe for swimming. Consumption For 10,000-gallon pools: add 4 lbs. to increase TA by 30 ppm; add 6 lbs. to increase TA by 40 ppm; add 7 lbs. to increase TA by 50 ppm; add 15 lbs. to increase TA by 100 ppm Jump to the detailed review |
| Calcium Hardness Adjuster | |
 Pool Mate Calcium Hardness Increase Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.7 Item form: Granular Net weight: 8 lbs. Active ingredients: 100% calcium chloride Packaging: Plastic bag | Purpose It is used to help increase the of the water. Too soft water can cause issues such as corrosion of metal fixtures, staining of pool surfaces, and reduced effectiveness of chlorine as a sanitizer. Consumption For 10,000-gallon pools: add 14.4 oz. to increase calcium hardness by 10 ppm; add 1.8 lbs. to increase calcium hardness by 20 ppm; add 3.6 lbs. to increase calcium hardness by 40 ppm; add 9 lbs. to increase calcium hardness by 100 ppm Jump to the detailed review |
| Clarifier, Flocculant & Algaecide | |
 Robarb Super Blue Clarifier Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.6 Item form: Liquid Net weight: 32 fl. oz. (1 qt.) Active ingredients: 65% sodium sulfate, 30% polyaluminum chloride, and 5% other ingredients Packaging: Plastic bottle | Purpose It is used to improve the clarity of pool water by removing small particles and debris that can make the water appear cloudy or dull. Consumption 2 oz. to treat 10,000 gallons Jump to the detailed review |
 In The Swim Super Pool Algaecide Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.6 Item form: Liquid Net weight: 32 fl. oz. (1 qt.) Active ingredients: 60% ethylene dichloride and 40% other ingredients Packaging: Plastic bottle | Purpose It is used to kill and prevent the growth of algae in swimming pools. Consumption 4 oz. to treat 10,000 gallons Jump to the detailed review |
 Characteristics Amazon Rating: 4.5 Item form: Liquid Net weight: 1.5 lbs. Active ingredients: aluminum sulfate Packaging: Plastic bottle | Purpose It is used to improve water clarity by causing small particles and debris to clump together and settle at the bottom of the pool. Consumption 1.5 lbs. to treat 10,000 gallons Jump to the detailed review |
Why Do I Need So Many Chemicals?

At first glance, it may seem that making water clean is very simple, like all you have to do is keep it safe from debris. However, clean water means water with balanced chemical levels: free available chlorine, pH, total alkalinity, calcium hardness, etc.
Unfortunately, there is no one-size-fits-all remedy because each chemical does one thing. For example, chlorine can’t raise the pH, and cyanuric acid can’t gather small debris in larger chunks. Also, sometimes you should adjust only one level (e.g., pH). For these reasons, there are many chemicals, each doing a specific job.
Which Ones Can Be Harmful to My Pool?
The answer to the question is the following: among the chemicals used for the pool maintenance, there are no dangerous products, but the wrong dosage can harm the water, the pool, and your health.
- Too much chlorine can damage pool liners and equipment.
- Adding too much muriatic acid (used to lower pH) can cause etching, corrosion, and damage to pool equipment.
- Too much calcium chloride (this is used to raise the calcium hardness level) can cause scaling on the pool’s surfaces and equipment.
These are not all possible examples, but the logic is easy to understand – you should measure the chemical levels in your pool and follow the instructions on how much and what to add.
Do Chemicals for Aboveground and Inground Pools Differ?

You can use the same chemicals to care for in-ground and aboveground pools. However, you should take into account a few factors that are distinctive to these two types:
- Size. Aboveground pools are usually smaller than in-ground pools because they come in fixed sizes, while the size of other types can vary. Therefore, you should use larger bags of chemicals for in-ground pools.
- pH. Aboveground pools can be made of vinyl or metal, so the pH of the water may be slightly lower than in in-ground pools. Therefore, chemicals for pH adjustment may be different.
- Chlorine. Aboveground pools are made of vinyl and plaster, so they require more careful use of chlorine, as this chemical can damage these finish types. Therefore, in in-ground pools, it is better to use non-chlorine shock.
Pool Sanitizers: Chlorine vs. Bromine
Pool sanitizer is one of the main chemicals in the maintenance cycle. You use it to kill bacteria and viruses and prevent algae growth that can cause infections and other harmful consequences for your health and pool.
There are two types of pool sanitizers: chlorine and bromine. The differences between them are significant. Firstly, they impact different chemical levels:
- Chlorine sanitizer. It impacts available chlorine, which is part of the total chlorine contained in the water not processed by bacteria, algae, and other organic matter. It has significant oxidizing and disinfecting power to keep the water clean and clear.
- Bromine sanitizer. It impacts free bromine, which is a part of total bromine not processed by bacteria, algae, and other organic matter. It also disinfects the water and kills bacteria.
Other differences you can find further in the article.
Chlorine – The Most Economical Sanitizing

The most economical sanitizing
| Characteristics | Item form: Tablets Net weight: 50 lbs. Proper level: 1–3 ppm Consumption: 1 tablet per 10,000 gallons Frequency of use: Once a week (or when < 1 or > 3) |
Chlorine is the most economical sanitizer because it will last almost twice as long as bromine. For one 10,000-gallon pool treatment, you should use one 8 oz. tablets. Therefore, you can do up to 100 treatments (almost two years) because you sanitize a pool once a week.
Also, according to user reviews, chlorine sanitizer has the highest efficiency rating: 80% versus 70% for bromine. Therefore, you can be sure that bacteria don’t stand a chance.
We recommend using In The Swim Stabilized Chlorine as this chemical has a #1 QC rating of its peers. One of the main reasons is its ease of use, as you only need to use one 3-inch tablet per 10,000 gallons. Moreover, they are packed in plastic bags that protect chlorine from moisture.
Pros
- Highest efficiency – chlorine is 10% more likely to provide an effective pool sanitizing
- Convenient packaging – each tablet is packed in a plastic bag, which makes it possible to protect them from breakage during transportation and storage
- Ease of use – add one tablet per 10,000 gallons, but if the tablets break, you can easily add the right amount of powder to the chlorination system due to the individual packaging
Cons
- Chlorine can irritate the skin and mucous membranes, so you should use it strictly following the instructions.
Bromine – The Safest Sanitizing

The safest sanitizing
| Characteristics | Item form: Tablets Net weight: 50 lbs. Proper free bromine level: 3–5 ppm Consumption: 1 tablet per 10,000 gallons Frequency of use: Once a week (or when < 1 or > 3) |
Bromine is the safest sanitizer. It is ideal for people with sensitive skin, as this chemical does not irritate the skin and mucous membranes, unlike chlorine. About 40% of users report that it is safe and easy on the skin, which is 20% more than chlorine. Moreover, bromine is less likely to corrode the pool equipment.
Another advantage is the ability to regenerate active bromine using an oxidizer such as potassium peroxymonosulfate, also called non-chlorine shock. To regenerate bromine, you need to take the following steps:
- Check active bromine level. If it is below 3 ppm, proceed to the next step.
- Add the required amount of non-chlorine shock. For example, you can use In The Swim Chlorine-Free Pool Shock and add one lb. per 10,000 gallons.
- Run the pump for 2–3 hours to evenly distribute the oxidizer.
- Test free bromine levels. If it is 3–5 ppm, everything is fine. Otherwise, repeat steps 2–4.
We recommend using In The Swim Bromine Sanitizer as it is the #1 chemical on the market. It has 20% more reviews for being safe for the skin and eyes.
Pros
- The safest for health – 20% of users admit that it doesn’t irritate skin and eyes
- Reduced chemical odor – 40% of users, which is 20% more than others, state that this chemical hasn’t got any bad odor
- Reusability – you can reactivate bromine using a non-chlorine shock
Cons
- You will spend up to two times more chemicals than when using a chlorine sanitizer
Chlorine & Non-Chlorine Shock
Pool shocking is a procedure that aims to remove a lot of bacteria, algae, and contaminants (cream, soap, etc.). However, there are two types of shock: chlorine and non-chlorine. The main difference lies in the different active ingredients:
- Chlorine shock. It often contains calcium hypochlorite, which, when added to water, quickly increases the level of available chlorine, killing bacteria and algae.
- Non-chlorine shock. It contains potassium peroxymonosulfate, which breaks the contaminants into smaller pieces, so the filter can separate them. Also, it removes , which form when chlorine reacts with sweat, makeup, and urine.
So, chlorine shock is most effective in removing bacteria, algae, and viruses, while non-chlorine shock is better suited to fight against contaminants and chloramines. However, there are many other differences between these two pool shock types, which we describe further in the article.
Chlorine – The Most Long-Lasting Result

The most long-lasting result
| Characteristics | Item form: Powder Net weight: 12 lbs. Proper level: 1–3 ppm Consumption: 12 lbs. per 13,500 gallons Frequency of use: Once a week (or when < 1 or > 3, after the rainfall, when opening/closing a season, and when algae are visible) |
Chlorine shock provides the most long-lasting result because it lasts up to three times longer than non-chlorine shock, as up to 60% of users report that they can shock the pool once every three weeks. Moreover, up to 80% of users note that this chemical effectively eliminates any algae: green, mustard, and black.
We recommend using HTH Super Shock as this chemical is 40% more effective at removing various algae, and 20% more users report results that last longer than other chlorine shocks (up to three days).
The manufacturer of HTH Super Shock recommends diluting it in a bucket of water before adding it to the pool so the chemical dissolves faster. However, users have also noticed that this extends the result for a longer period:
“The effectiveness increases when I pre-dissolve shock in a bucket. Manufacturers advise you to do that to protect the liner. However, I’ve discovered that, in roughly comparable circumstances, pre-mixing the free chlorine, made it last longer.“
AB, Amazon User
Pros
- The most long-lasting result – one treatment lasts up to three weeks, which is three times longer than other
- Effective algae removal – 80% of users, which is 40% more than non-chlorine shock has, state that it can effectively eliminate green, mustard, and black algae
- Safe for equipment – 20% of users, which is 10% more than non-chlorine shock has, admit that it will not spoil the pool equipment
Cons
- Some cloudiness may appear after adding a chlorine pool shock, but it is OK, so you should not worry and wait for 1–2 hours before it disappears
Non-Chlorine – The Most Effective Chlorine Level Adjustment

The most effective chlorine level adjustment
| Characteristics | Item form: Tablets Net weight: 40 lbs. Proper level: 1–3 ppm Consumption: 1 tablet per 10,000 gallons Frequency of use: Once in 1–2 weeks (or when < 1 or > 3 after the rainfall or heavy pool usage, and when algae are visible) |
Non-chlorine shock is the most effective in adjusting free chlorine levels, as 80% of users state that it effectively keeps free chlorine levels
Also, non-chlorine shock allows you to regenerate bromine effectively since one of the active substances is potassium peroxymonosulfate. This substance reacts with bromine and turns it into a sanitizer, which also helps fight bacteria, algae, and contaminants.
We recommend using In The Swim Chlorine-Free Pool Shock as this chemical is #1 among others and is up to 80% more effective at adjusting free chlorine levels and regenerating bromine. Also, it allows you to sanitize water in a couple of hours:
“I shall never be without this fantastic shock because I love it so much. I shock the pool once a week when my kid comes in for lunch. He will be able to swim in the pool once he finishes his lunch.”
— Michael C. Doman Sr., PA
Pros
- The most effective free chlorine levels adjusting – 80% of users state that it efficiently adjusts free chlorine levels, which is up to 70% more than others
- No bad odor – it efficiently eliminates chloramines, which are the main cause of bad chlorine smell
- Safe for other chemical levels – 40% of users state that it doesn’t affect other chemical levels
Cons
- It is $0.1 per 1 oz. more expensive than chlorine shock, so you should pay approximately $1.6 more per 1 lb.
Cyanuric Acid And Why It Is Called Stabilizer
Cyanuric acid is called a stabilizer because it protects chlorine from losing its effectiveness when affected by sunlight. Ultraviolet light destroys the chlorine shell, which, in turn, reduces the level of available chlorine and threatens to increase the number of bacteria in the water.
Cyanuric acid creates a protective coating around the chlorine, which prevents ultraviolet radiation from negatively impacting the chlorine.
We recommend using Pool Mate Stabilizer and Conditioner as this chemical, according to user reviews, scores almost 100% efficiency in adjusting cyanuric acid levels.
| Item |  Pool Mate Stabilizer and Conditioner |
| Characteristics | Item form: Powder Net weight: 7 lbs. Proper level: 30–50 ppm Frequency of use: Once a month test CA levels, and if they are out of the 30–50 ppm range, add a stabilizer |
| Consumption per 10,000 gallons | 12.5 oz. to increase by 10 ppm; 1.6 lbs. to increase by 20 ppm; 2.3 lbs. to increase by 30 ppm; 3.1 lbs. to increase by 40 ppm; 3.9 lbs. to increase by 50 ppm |
pH & Total Alkalinity Adjusters
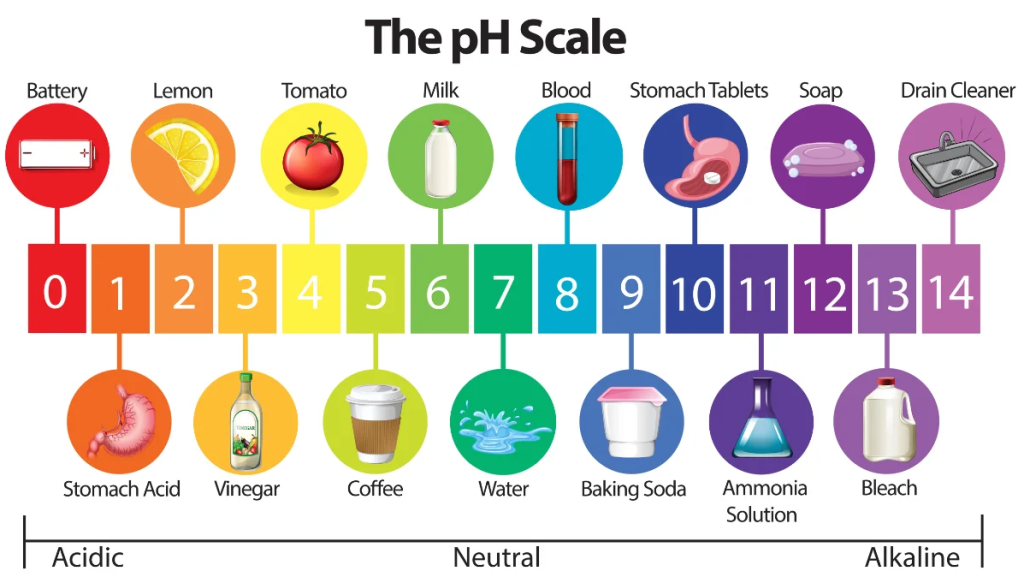
pH is one of the most basic levels and should be measured at least once a week, as incorrect pH can make other chemicals ineffective. In general, pH is a measure of how alkaline or acidic water is. You need to maintain levels between 7.2 and 7.8 to protect your health and the condition of the pool and equipment.
In the table below, we have indicated why low and high pH are harmful and how you can adjust them:
| Item |  Clorox Pool&Spa pH Up |  Clorox Pool&Spa pH Down |
| Consumption per 10,000 | 12 oz. to increase pH from 6.8–7.1 to 7.2–7.6; 16 oz. to increase pH from 6.5–6.7 to 7.2–7.6; 30 oz. to increase pH from 6.4 and below to 7.2–7.6 | 6 oz. to lower pH from 7.7–7.8 to 7.2–7.6; 12 oz. to lower pH from 7.9–8.0 to 7.2–7.6; 20 oz. to lower pH from 8.1–8.4 to 7.2–7.6; 24 oz. to lower pH from 8.5 and above to 7.2–7.6 |
| Why to use in case of improper levels | pH below 7.2. Firstly, it is dangerous for the swimmer's health, as it can cause skin and eye irritation. Secondly, it reduces the effectiveness of chlorine. Thirdly, it can damage the pool finish and equipment. | pH above 7.8. Firstly, it can cause scale formation on the pool finish and equipment. Secondly, it may be the reason for the decrease in the effectiveness of chlorine and the appearance of cloudiness. |
Total alkalinity is closely related to pH, since this indicator characterizes the stability of the pH. Thus, if the TA is in the acceptable range of 80 to 120 ppm, the pH will be easier to adjust. When TA < 80 ppm, the levels will constantly fluctuate, and, when > 120 ppm, the water will be too alkaline, so the pH will also be high. Keep in mind that to lower levels, you can use pH decreasers like muriatic acid or sodium bisulfate.
| Item |  Clorox Pool&Spa Alkalinity Increaser |
| Characteristics | Item form: Granular Net weight: 5 lbs. Proper pH level: 80–120 ppm Frequency of use: If you notice unpredictable changes in pH levels, test levels, and if needed, add an adjuster |
| Consumption per 10,000 gallons | 4 lbs. to increase TA by 30 ppm; 7 lbs. to increase TA by 50 ppm; 12 lbs. to increase TA by 80 ppm; 15 lbs. to increase TA by 100 ppm |
Calcium Hardness Adjusters
Calcium hardness is also an important indicator that you should monitor regularly. It characterizes the amount of dissolved calcium in the water, and the normal one is from 200 ppm to 400 ppm. If < 200 ppm, the water becomes too aggressive and can damage the pool finish or equipment, and if > 400 ppm, a scale will appear that can damage the pool’s equipment.
We recommend using the Pool Mate Calcium Hardness Increaser, as this item is #1 among the rest, as almost 100% of users report its effectiveness.
| Item |  Pool Mate Calcium Hardness Increaser |
| Characteristics | Item form: Granular Net weight: 8 lbs. Proper level: 200–400 ppm Frequency of use: Once a month test levels, and if they are out of the 200–400 ppm range, add an adjuster |
| Consumption per 10,000 gallons | 14.4 oz. to increase CH by 10 ppm; 2.7 lbs. to increase CH by 30 ppm; 5.4 lbs. to increase CH by 60 ppm; 9 lbs. to increase CH by 100 ppm |
Clarifier, Flocculant, Algaecide & Their Differences
Clarifiers, flocculants, and algaecides are highly targeted chemicals designed to fix specific problems. We have gathered a detailed comparison to help you sort out and understand the difference between the chemicals.
 Robarb Super Blue Clarifier |  In The Swim Super Pool Algaecide |  Baquacil Flocculant |
|
| Purpose | To clear cloudy or hazy water | To prevent or kill algae | To clear cloudy or discolored water |
| Cleaning rate | 12–24 hours | 24 hours | 10–12 hours |
| Consumption per 10,000 gallons | 2 oz. | 4 oz. | 1.5 lbs. |
| Frequency of use | Irregular intended use | Weekly or bi-weekly to prevent algae growth | Irregular intended use |
| Principle of working | Cause particles in the pool water to clump together and go to the top of the pool, so they can be easily filtered out | Contain chemicals dangerous for algae, which prevent their growth and reproduction | Cause small particles in the pool water to clump together and settle to the bottom |
In What Order to Add Pool Chemicals?

The correct order of adding chemicals to a pool can vary because you rarely need to use everything at once. However, the recommended order can be specified as follows:
- Adjust pH. Proper pH levels are the foundation for further water treatment. Measure it using test kits, and if the pH is not 7.2–7.8, apply adjusters.
- Total alkalinity. A properly adjusted TA will keep your pH stable. Measure levels, and if TA is not 80–120 ppm, apply adjusters.
- Calcium hardness. Measure CA levels and adjust to 200–400 ppm if necessary.
- Stabilizer. Use it to protect chlorine from ultraviolet in advance. Your goal is 30–50 ppm of cyanuric acid.
- Sanitizer. You can use either bromine or chlorine to reach the appropriate levels: 3–5 ppm of active bromine and 1–3 ppm of free chlorine.
- Shock. Shock the pool regularly to kill bacteria and algae. However, keep in mind that your chlorine and bromine levels must match those previously indicated.
- Clarifier or flocculant. Only add if your water is cloudy or hazy. Otherwise, you will not achieve any effect or destabilize the levels.
- Algaecide. Depending on the product, add regularly or as needed to kill algae.
Summary
Each time, different factors can cause the water not to be clear. For this reason, you can’t use one chemical that will always treat the pool. Therefore, to keep your pool water safe and sparkling, you might need to use nine different chemicals.
In this article, we have gathered all the necessary pool chemicals, explained in detail why each is needed, and indicated in what order to add them to the pool. If you missed something from the above, we suggest you familiarize yourself.
See you in the next articles!
FAQ
💊 What chemicals do you need for a pool?
To keep your water sparkling clean, you should use the following chemicals: sanitizer, shock, stabilizer, pH, total alkalinity and calcium hardness adjusters, clarifier, flocculant, and algaecide. You can find more info in our article.
🦠 What is the best chemical for a dirty pool?
Usually, a shock is used to clean a dirty pool. However, we recommend checking all levels, as the cause of contamination may be the destabilization of the chemical levels.
🟢 What chemicals to put in a green pool?
If your pool has turned green, chances are it has algae in it. In such a case, you can use an algaecide. However, we recommend that you check the levels initially, as the problem could be incorrect pH, total alkalinity, or low free chlorine levels.
🏊♀️ Can I swim in my pool without chemicals?
We strongly discourage you from swimming in a pool that is not treated with chemicals, as this puts you at risk of contracting infections, viruses, etc.


